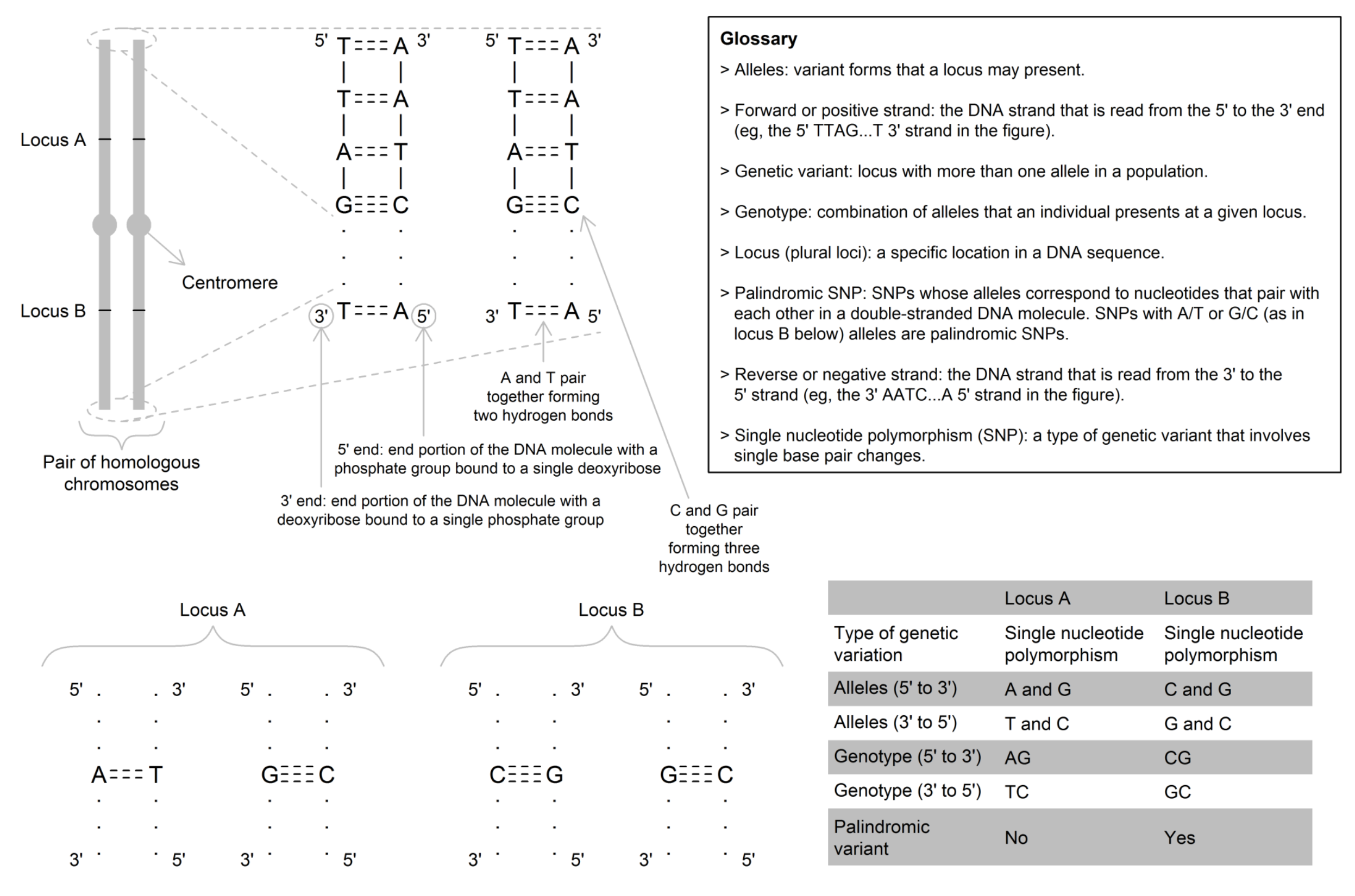
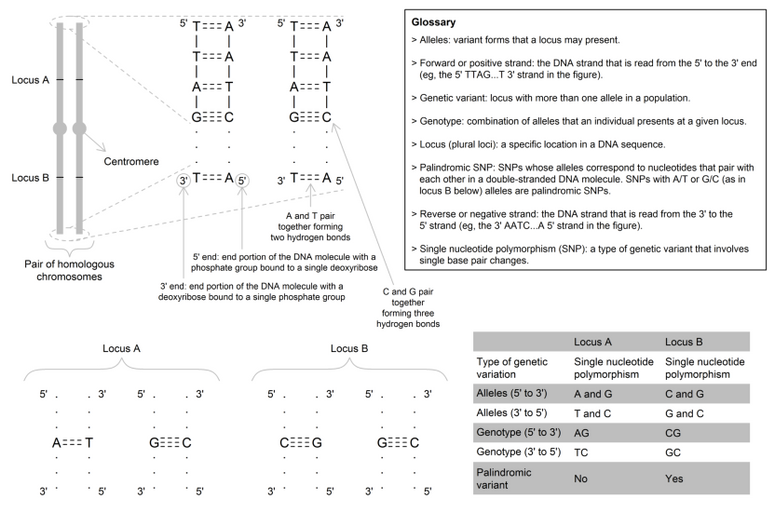
A deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule that carries a portion of all genetic material. Two homologous chromosomes carry the same collection of genes, but each gene can be represented by a different allele on the two homologues (i.e., a heterozygous individual). A gamete (egg or sperm) will receive one of these homologues, but not both. Humans have 22 pairs of autosomal homologous chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes.
Used to identify the position of a genetic variant that may be used within MR studies as an instrumental variable (IV).
References
Other terms in 'Useful genetic terms ':
- Allele
- Cis- and trans-variants
- Copy number variation
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Gene
- Genetic variant
- Genotype
- Haplotype
- Heterozygous or Heterozygote
- Homozygous or Homozygote
- Linkage disequilibrium (LD)
- Locus
- Palindromic single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
- Polygenic risk score (PRS)
- Polymorphism
- Rare variants
- Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)