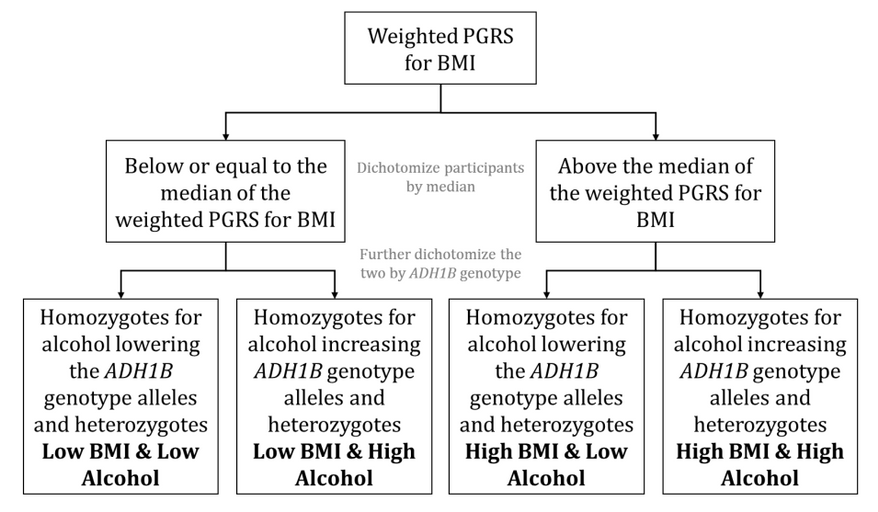
An MR method that explores the separate and joint causal effects of two (or potentially more) exposures on an outcome and is analogous to factorial randomized controlled trial (RCT) designs. Participants in a factorial MR study are categorised into different levels of each exposure based on their genetic instrumental variables (IVs). Where the genetic IV involves multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), categories of high versus low exposure might be defined by being above and below the median of a polygenic risk score (PRS) comprising those SNPs. For a genetic IV that includes a single SNP, the categorisation may be two groups (i.e., one group of homozygotes versus a group of the heterozygotes and other homozygotes together) or three groups (i.e., homozygotes for one allele, heterozygotes, and homozygotes for the other allele). Regression analyses are then conducted with the genetic IV categories.
Genetic IVs for the two (or potentially more) exposures are the categories defined by genetic variants associated with those exposures. These categories need to fulfil the key MR assumptions. Factorial MR may have limited statistical power (in comparison to factorial RCTs and MR of single exposures).
References
- Carter AR, Borges MC, Benn M, et al. Investigating the combined association of BMI and alcohol consumption on liver disease and biomarkers: a Mendelian randomization study of over 90,000 adults from the Copenhagen General Population Study. bioRxiv 2018; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/303313
- Ference BA, Majeed F, Penumetcha R, Flack JM, Brook RD. Effect of naturally random allocation to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on the risk of coronary heart disease mediated by polymorphisms in NPC1L1, HMGCR, or both: a 2 x 2 factorial Mendelian randomization study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 65: 1552-61.
Other terms in 'Definition of MR and study designs':
- Bidirectional MR
- Instrumental variable (IV)
- Mendelian randomization (MR)
- MR for drug targets
- MR with binary exposures
- Multivariable MR
- One-sample MR or MR with individual-level data
- Two-sample MR or MR with summary-level data
- Two-step or Mediation MR

