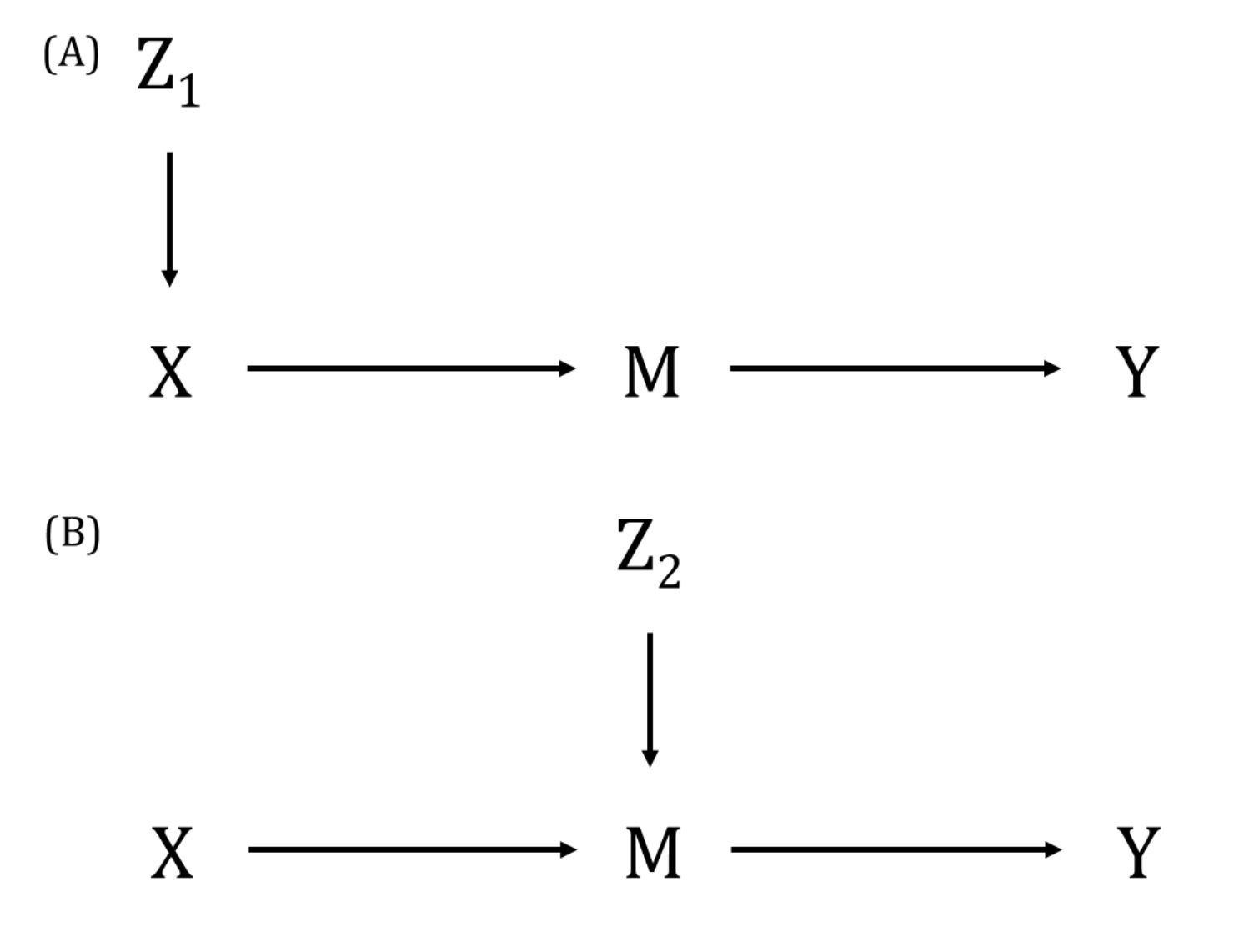An MR framework that aims to quantify whether an exposure-outcome association (that is either established or has supportive evidence from MR analyses) is mediated by another factor.
In many published examples, initial MR will assess evidence for a causal effect of the exposure on an outcome and then go on to undertake two-step MR. First, genetic instrumental variables (IVs) associated with the exposure are used to determine the causal effect of the exposure on the potential mediator (step one). Secondly, genetic IVs associated with the potential mediator and independent of those used for step one are used to determine the effect of the potential mediator on the outcome of interest (step two). Alternatively, multivariable MR can be used for the second step to estimate the direct effect of both the exposure and mediator on the outcome. Methods such as the product-of-coefficients can then be used to explore the extent of this mediation. The MR assumptions must be met for the two steps of the MR analyses of the (i) exposure on mediator and (ii) mediator on outcome. This methodology can be extended to networks of relationships (i.e., network MR).
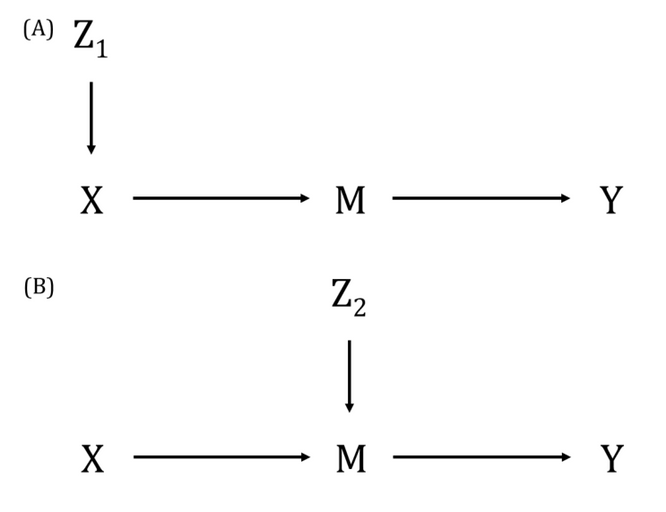
References
- Burgess S, Daniel RM, Butterworth AS, Thompson SG, Consortium EP-I. Network Mendelian randomization: using genetic variants as instrumental variables to investigate mediation in causal pathways. Int J Epidemiol 2015; 44: 484-95.
- Richmond RC, Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey Smith G, Relton CL. Challenges and novel approaches for investigating molecular mediation. Hum Mol Genet 2016; 25: R149-R156.
- Relton CL, Davey Smith G. Two-step epigenetic Mendelian randomization: a strategy for establishing the causal role of epigenetic processes in pathways to disease. Int J Epidemiol 2012; 41: 161-76.
- Xu L, Borges MC, Hemani G, Lawlor DA. The role of glycaemic and lipid risk factors in mediating the effect of BMI on coronary heart disease: a two-step, two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 2017; 60: 2210-2220.
Other terms in 'Definition of MR and study designs':
- Bidirectional MR
- Factorial MR
- Instrumental variable (IV)
- Mendelian randomization (MR)
- MR for drug targets
- MR with binary exposures
- Multivariable MR
- One-sample MR or MR with individual-level data
- Two-sample MR or MR with summary-level data